IT security is all about how to best secure your information. With a number of attacks happening over the course of 2016, we learnt that everything can be at risk - from customer related data sitting in your network to the photos saved on your phone.
Unauthorized access to information (hacking) has been on the rise in the last few years. In this post, we picked our technical director's brain and collected a number of factors and predictions for the year ahead.
But first, why should you care about IT security?
Well, according to the 2015 ITRC Data Breach Report, over 169 million personal records were exposed in 2015, stemming from 781 publicized breaches across the financial, business, education, government and healthcare sectors.
In another words - no organization (or person) is safe, regardless of how large or small their IT team is.
Sounds like a cheesy line from a bad horror film, doesn’t it? Don’t worry, though! Despite a bleak-sounding world, there are precautions you can take to avoid the hackers and keep your personal data safe. We’ll walk you through every trend and precaution – let’s begin!
Breach #1: Ransomware
First on the list of IT security trends is a malicious software known as Ransomware. This software, as the name implies, is used to block access to a computer system (i.e. “hold it for ransom”) until a sum of money has been paid.
Ransomware has been the biggest contributor to IT Security breaches in 2016, an alarming average of 40,000 attacks per month were reported, with an estimated $1 billion paid to ransomware criminals.
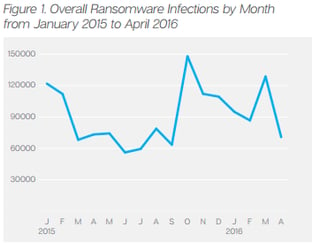 Source: Symantec
Source: Symantec
Ransomware in 2017 – What is the trend?
Let's just start by saying that there is no doubt that Ransomware will be very high on the list of IT security breachs in 2017. There are numerous versions of Ransomware out there generated and operated by highly motivated criminal outfits. (We’re building up to a seriously good action flick, aren’t we?)
A new trend of exposing decryptions keys of different ransomware was seen in 2016.
In normal-person speak, that looks like this:
- When people get a ransomware, that means someone got into their computer and encrypted (or password protected) a file.
- The hacker then asks for money to decrypt (unlock) it.
- You pay the money
- They give you a decryption key, which unlocks the file/your computer
These were mostly released by competing groups who hacked into each other’s systems. The hackers are doing this as a business, so they compete with other hackers by hacking each other.
Going forward, Ransomware attacks will be on the rise and will gain maturity as we head into 2017. Attackers are not only sending random emails to a number of users, they are also doing their research and finding publically available information about their targets before coming up with the email’s content.
In other words, if you love puppies, they can exploit that and send you images of puppies to your email. Beware of puppies… or just emails that seem perfectly tailored to things you like from sources you’re unsure of.

⇒ Here's an example of how this happens every day
Staying true to our action movie (which seems to be turning into a spy movie), here’s a real-life example that might shock you:
Hackers can find out if one of your directors is on holiday and then spoof their email address (i.e. making it seem like the email is coming from the director). They will then send a casual holiday-type email to the accounting department, asking to transfer money to one of their trading partners in Hong Kong
Sound crazy? Yes. Does it really happen? Yes.
⊕ How to protect yourself ⊕
Ignorance may be bliss, but it also blinds you and makes you vulnerable. Education is the key to stopping (or at least decreasing) these Ransomware attacks. End users need to have the knowledge to spot a fake email or website link, or at least know who to ask for help.
There are also some clever methods being used by major security providers to detect and quarantine Ransomware emails. For example, Microsoft’s Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) uses a sandbox environment for their Exchange Online product.
This tool ensures any URLs in email messages are rewritten so that users are redirected through a Microsoft service that checks the link for malicious content when the user clicks it. In another words, it's like automatic hacker protection!
Breach #2: Smart Devices & IOT
The popularity of smart devices (like watches, glasses, and even household appliances) is blowing up as we discover how to connect everything. People are enjoying the convenience of being able to do more without having to get off the couch (we’re getting closer and closer to being like the Jetsons every year).
Unfortunately, the IOT (Internet of things) is another entry point for hackers to steal private information. As more devices are converted into smart devices by enabling remote access, they are also becoming vulnerable to potential attacks via the internet.
Recently (Sep 2016), attackers used an army of hijacked security and video cameras to launch a coordinated attack on various websites, rendering them offline or unusable. Traditionally, these types of attacks were launched from hijacked computers. However, this was one of the first (and largest) attacks of its kind that used smart devices.
With a need and demand for everything to be online and accessible, millions of devices can now be accessed from the internet, creating another vector for hackers to exploit.
So, what’s the trend?
We suspect this is just the beginning and there will be an increase in the number of attacks, either to these devices themselves or to other hosts using them.
With the smart device market being highly competitive and filled with thousands of different brands, it’s difficult to regulate the market and to force companies to build security into their devices.
⊕ How to protect yourself ⊕
Like any device we buy, there are some simple steps to reduce the risk of being hacked. First, change the default username/password used to control the device. Time and time, we see devices being configured with their default username/password, which makes it very easy for the hackers to take control and exploit them.
The other trick is to make sure the device’s software is up to date. Most of the vendors supply updated software for their devices with improved security and it’s essential to apply these as soon as possible. This not only stops hackers from exploiting security holes, but can also add some cool new features!
Breach #3: Increased Attacks on Mobile Devices
Just as smart devices are at risk, so too is the little rectangle in your pocket every day. It’s hard (basically impossible) to deny that mobile devices are now an integral part of our lives. With an ever-increasing processing power and constant connectivity, phones are now ideal targets for hackers (even more so than traditional computers!).
It’s estimated that, on average, US smartphone and table users spend 4.7 hours per day on their devices. [Source Digitaltrends].
It’s becoming evident that Android is targeted by the majority of these hacks, as it runs on roughly 80% of devices around the world.
The trend: Attacks will increase in 2017!
We expect this trend to continue in 2017 as more groups find ways to compromise both of these systems. And, if the following analysis is correct, more vulnerabilities will be exploited in Android than iOS due to the lax requirements to get an app on the Android app store.
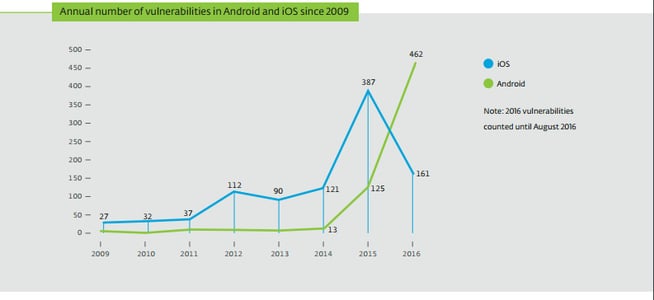 Source: www.cvedetails.com
Source: www.cvedetails.com
Apps, being plentiful on nearly every device, are one of the main entry points into mobile devices by attackers. As exponentially more apps are created, it’s getting more difficult for both iOS and Android app stores to verify the authenticity and intent of the app developer.
However, both Android and iOS have taken large strides towards tightening the security and making sure there are no holes to be taken advantage off.
⊕ How to Protect Yourself ⊕
There are few ways users can protect themselves from these malicious attacks:
- Just as you did with your smart devices, make sure your mobile devices are up-to-date with the latest updates. As mentioned above, both Apple and Google dedicated a lot of resources to fix any holes in their security, so take advantage of these free updates!
- Secondly, since most hackers disguise their code inside apps, always do your research before blindly installing an app! Look out for the number of users who have downloaded the app and check for reviews. This will give you a good indication on the legitimacy of the app.
- Also, look out for the permissions the app requires when it’s installed for the first time. For example, if you are installing a calculator app and it asks for access to your camera and photos, then you should know something’s not right.
Breach #4: Risks to Dinosaur IT Systems

Source: Wikimedia Commons
There is a huge risk to old IT systems used by large enterprises all over the world. Some of these systems were developed in the 80s with less attention to security.
With the need to modernize these systems on a limited budget, companies are adding new modules to them, rather than developing them from ground up. This increases the risk, as the old code is still in place with vulnerabilities.
Prime examples include Hotel and Air Line booking systems. Both of these kind of systems were developed in the 80s to increase business efficiencies and streamline the processes. However, with increased use of the internet over the last decade, they’ve been forced to add layers which provide user-friendly access to these backend systems.
The main problem with such modernization is that it doesn’t fix any inherent security issues. For example, it’s very easy for someone to use the 6-digit code on your booked luggage sticker to get all of your personal information from the Air Line’s database [Source SRL].
The same is true with Hotel booking systems, where the loyalty programs have been hacked very easily and user’s points are donated to a third party who then converts them into cash rewards, etc. We expect to see a rise in attacks on these dinosaur systems as they become more accessible (and companies continue to look for ways to cut costs).
⊕ How to Protect Yourself ⊕
Unfortunately, it’s very difficult to protect against these types of attacks. Even if we could somehow hide our baggage tags or only have carry-on baggage, hackers can still use brute force attacks against these old systems to get personal information about travelers.
The only solution is for these giant industries to look at modernization of these backend systems. Unfortunately, that’s something many corporations don’t think about, but it all comes down to their priorities and how big of a problem it is for their end users.
Breach #5: Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) was a big hit in 2016 with the introduction of Pokémon Go (sound familiar?) and Microsoft’s HoloLens. We suspect plenty more apps and products will follow suite, and 2017 will be an even bigger year for AR.
As you can imagine, the great thing about AR is that it mixes real life with a virtual one and allows the end user to immerse themselves in an experience. Eventually, we may not be able to differentiate between virtual and real. Sounds like the Matrix, right?
However, this also is the biggest problem with AR - it can easily be exploited by hackers.
Hacking or exploitation of AR systems is more dangerous than a normal computer hack because it not only messes with our virtual world, but also our physical world. It can lead us onto busy roads or to leap from the edge of a building. It can make us think there are physical objects present when they are not actually there. Yikes!
⊕ How to Protect Yourself ⊕
So far, we have not seen any major attacks or exploitation of these system. However, having the knowledge of its possibility alone can make a big difference in how we use AR going forward. Just keep your eyes open!
⤷ Multi-Factor Authentication Systems… A Solution to The Problem?
One of the main methods of providing an extra layer of security when accessing sensitive systems has always been 2-factor authentication. This is where an end user is asked to provide an extra piece of information alongside their username and password when logging into a system.
In the past, it’s always been a hard token-based service like RSA SecurID. However, that’s been changing over the last few years. More companies are adopting the use of virtual tokens (such as Google Authenticator), which are basically apps installed on their mobile devices that provide the same log-in token as a physical device would.
With more and more applications being migrated to cloud, 2-Factor Authentication is gaining popularity and becoming more affordable.
In year 2017 we expect more adoption of 2-factor authentication as well as introduction of other factors used in conjunction. For example, Microsoft Office 365 is coming up with the option to restrict user log-ins from certain locations [Source Linkedin]. These options could also include biometric scans e.g. finger, retina, etc. (Hello, Matrix! We’ve been waiting for you.)
Conclusion
It goes without saying that IT security is on everyone’s mind. With centralization of data and greater accessibility to devices, malicious groups now have a lot more attack vectors than ever before.
We live in an era where a hacker sitting in their bedroom accross the world has the potential to gain access to the baby monitor at your house.
Security attacks in 2016 were led by an increase in specialized Ransomware attacks. We also witnessed the inception of attacks using connected devices, such as security cameras. 2017 won’t be any different in terms of increases in these types of attacks. Additionally, some new venues will be exploited by hackers.
The good news is that everyone in the IT industry is focused on finding solutions to counter these attacks.
IT Security is not an afterthought anymore, but rather, a necessity.
Click to Tweet ![]()
User education, however, remains the best defense against all these attacks. Your staff needs to be aware of different types of attacks and the steps they can take to reduce their risk. As end users, we cannot simply rely on security experts and vendors to protect us. They can only provide us the tools - it’s up to us to make sure we understand and use them to protect ourselves.
♥ And here's one last give away from us ♥







